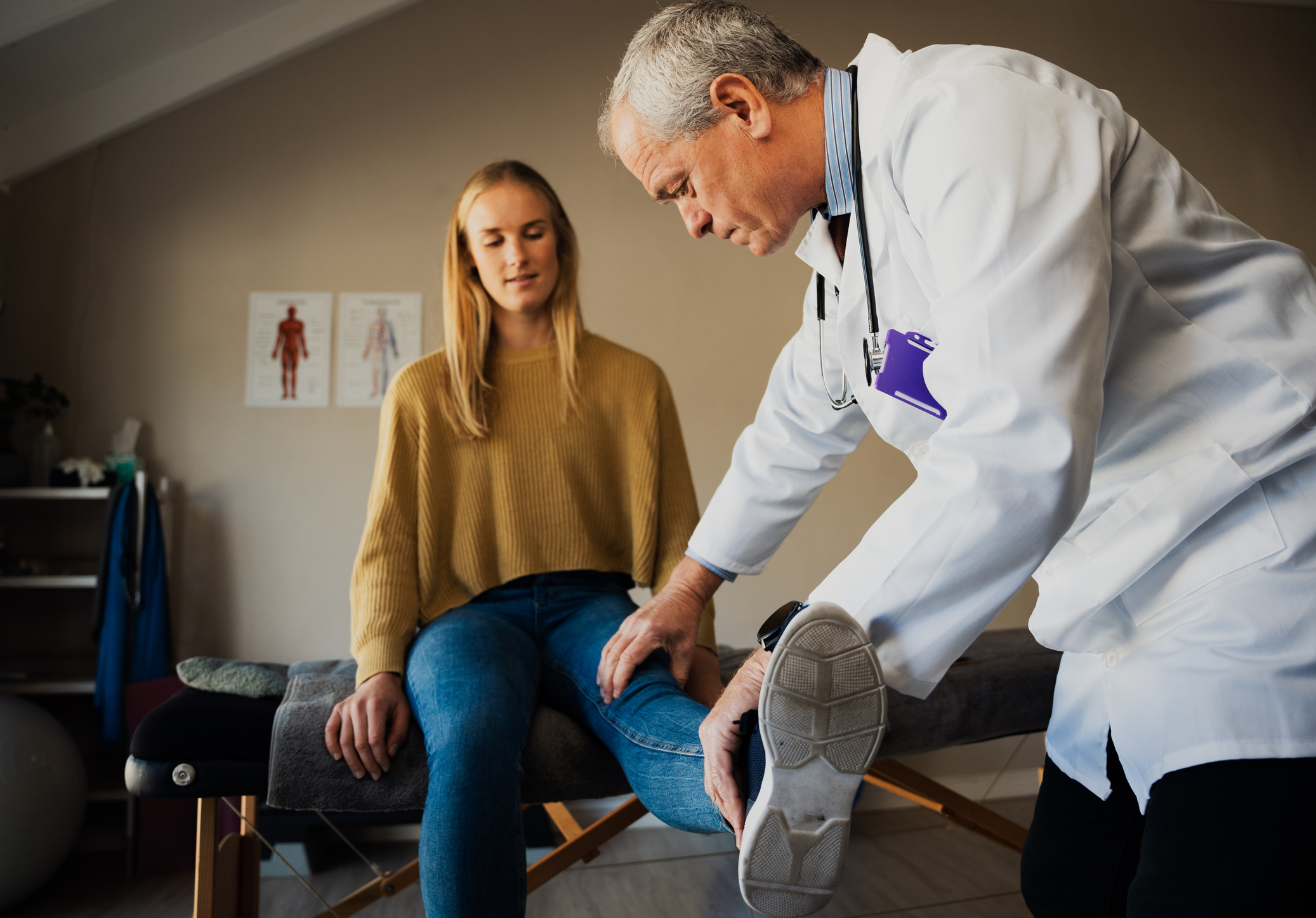
Shoulder Pain: Symptoms, Causes and Risk Factors
Shoulder Pain: Symptoms, Causes and Risk Factors
Everyone hates that twinge in the shoulder—you know the one. It can start as a minor annoyance and quickly escalate, limiting your ability to reach for a coffee cup, throw a ball, or even find a comfortable sleeping position. Shoulder pain is incredibly common, affecting most people at some point in their lives. This widespread experience is no surprise, considering the shoulder’s remarkable range of motion.
As the body’s most mobile joint, the glenohumeral joint empowers our arms to perform a vast array of movements, from delicate tasks to powerful swings. But this very mobility also makes it vulnerable to injury and pain.
From minor muscle strains picked up during a weekend gardening project to more serious conditions like rotator cuff tears or even heart attacks, shoulder pain can stem from a variety of causes. Understanding the complex anatomy of the shoulder—the intricate interplay of bones, muscles, ligaments, tendons, nerves, and blood vessels—is key to understanding why so many things can go wrong.
Let’s explore the common culprits behind shoulder pain, delve into the symptoms to watch out for, and outline the risk factors that can make you more susceptible to shoulder problems.
What Causes Shoulder Pain?
Shoulder pain can be triggered by a variety of factors, affecting any of the structures within and surrounding the joint. These causes can range from acute injuries to chronic conditions. Pinpointing the specific cause is often key to effective treatment.
Musculoskeletal Causes
These causes relate to the muscles, tendons, ligaments, and bones of the shoulder complex:
- Overuse Injuries: Repetitive motions, especially overhead activities like painting or throwing, can strain muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
- Rotator Cuff Tears: These tears, affecting the group of muscles and tendons stabilizing the shoulder joint, are a common source of pain and weakness.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae (fluid-filled sacs that cushion the joint) can cause pain and stiffness.
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of the tendons, often due to overuse, can lead to pain and restricted movement.
- Fractures: Breaks in the bones of the shoulder (humerus, clavicle, or scapula) can result from falls or other trauma.
- Shoulder Dislocation: The humerus can be forced out of its socket, causing significant pain and instability.
- Frozen Shoulder: This condition, characterized by stiffness and pain, limits the shoulder’s range of motion.
Diseases & Conditions
These causes involve broader medical conditions that can manifest as shoulder pain:
- Arthritis: Conditions like osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis can damage the shoulder joint, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion.
- Nerve Compression: Nerves in the shoulder or neck can become compressed, leading to pain, numbness, or tingling.
- Referred Pain: Sometimes, pain originating elsewhere in the body, such as from the neck or heart, can be felt in the shoulder.
What Are Shoulder Pain Risk Factors?
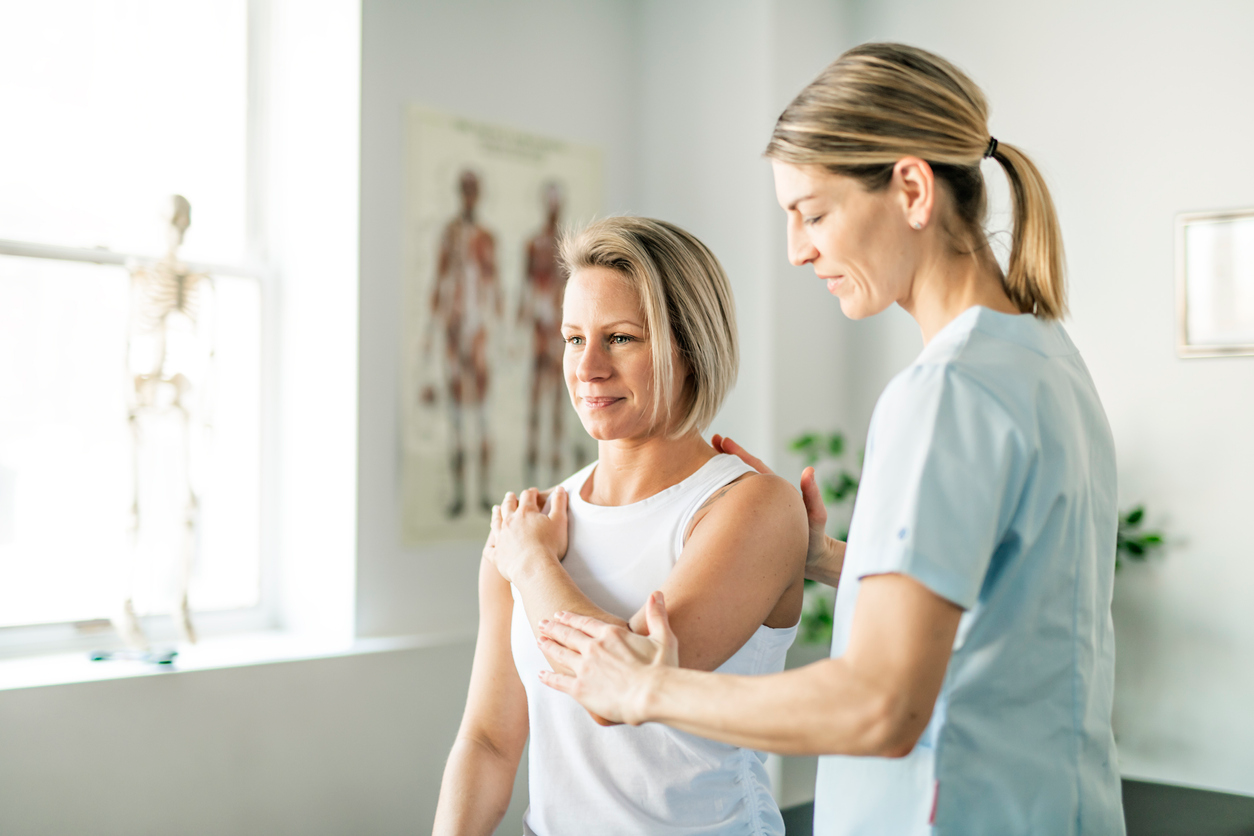

While anyone can experience shoulder pain, certain factors can increase your risk. Age plays a role, as wear and tear on the shoulder joint naturally accumulates over time, making tendons and ligaments more susceptible to injury.
Repetitive overhead activities, common in certain jobs (like painters, carpenters, and athletes), significantly elevate the risk of overuse injuries like rotator cuff tears and tendinitis. Previous shoulder injuries, even seemingly minor ones, can weaken the shoulder joint and predispose it to future problems. Poor posture can also contribute, as it can place undue stress on the shoulder and surrounding muscles.
Beyond lifestyle and occupational factors, certain medical conditions can also increase your risk of shoulder pain. Diabetes, for instance, has been linked to an increased likelihood of developing frozen shoulder. Similarly, autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis can cause inflammation and damage within the shoulder joint.
Genetics may also play a role, as some individuals may be predisposed to certain shoulder conditions due to inherited factors. Understanding these risk factors can empower you to take proactive steps to protect your shoulders and minimize your chances of experiencing pain.
Musculoskeletal Causes of Upper Arm Bone and Shoulder Pain
Shoulder pain may be caused by injury or disease of the muscles, bones, tendons or ligaments of the shoulder, neck, or upper arm including:
- Activities involving constant, repetitive shoulder use
- Arthritis including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout
- Bone fractures, such as a fractured humerus (upper arm bone) or collarbone (clavicle)
- Bursitis (inflammation of fluid-filled sacs that protect joints and allow movement)
- Cervical spondylosis (degeneration of bones and cartilage in the neck)
- Fibromyalgia (chronic condition causing pain, stiffness and tenderness)
- Frozen shoulder syndrome (muscles, tendons and ligaments become stiff resulting in painful and difficult movement)
- Poor posture or keeping the shoulder in an abnormal position for long periods, such as when sleeping
- Rotator cuff tear or rotator cuff tendonitis (inflammation of the tendons of the rotator cuff)
- Shoulder joint dislocation or shoulder separation (tearing or stretching of ligaments)
- Shoulder or upper arm muscle strain
- Whiplash (sprained or strained neck)
Questions for Diagnosing the Cause of Shoulder Pain
To diagnose your condition, your doctor or licensed health care practitioner will ask you several questions related to your shoulder pain. Providing complete answers to these questions will help your health care provider determine the cause of your shoulder pain. Questions include:
- In what part of the shoulder do you feel pain?
- When did the shoulder pain start?
- How long does the shoulder pain last?
- Are there any activities that cause the shoulder pain?
- Are you experiencing any other symptoms?
- Have you had any trauma to the shoulder?
- What are the potential complications of shoulder pain?
Complications associated with shoulder pain and its underlying cause can be progressive. In some cases, shoulder pain may become a chronic condition and affect your daily life. Once the underlying cause is determined, following the treatment plan outlined by your doctor can help reduce any potential complications including:
- Absenteeism from work or school
- Disability
- Permanent nerve damage
- Poor arm and shoulder movement
- Poor quality of life
Get Expert Orthopedic Care for Shoulder Pain in Chapin, SC
At Palmetto Bone & Joint, we pride ourselves on our ability to restore our patients to sporting shape. From fluke sports injuries to total joint replacement, we combine the latest orthopedic technologies and methods with our outpatient Chapin Surgery Center to get you back and moving in no time flat.
If you’ve been dealing with shoulder muscle pain, elbow pain, stiffness, swelling, or tenderness, schedule your appointment with the orthopedic specialists at Palmetto Bone & Joint today.